Unix Introduction
What is Unix?
Unix is an operating system which was first developed in the 1960s, and has been under constant development ever since.
By operating system, we mean the suite of programs which make the computer work. It is a stable, multi-user, multi-tasking
system for servers, desktops and laptops.
Unix systems also have a graphical user interface (GUI) similar to Microsoft Windows which provides an easy to use
environment. However, knowledge of Unix is required for operations which aren't covered by a graphical program, or for
when there is no windows interface available, for example, in an SSH session.
Types of Unix
There are many different versions of Unix, although they share common similarities. Popular varieties of
Unix include Oracle's Solaris, Linux, and macOS.
The two Unix machines used in this class, turing and hopper, are running Debian Linux.
The Unix Operating system
The Unix operating system is made up of three parts; the kernel, the shell and the programs.
The Kernel
The kernel of Unix is the hub of the operating system: it allocates time and memory to programs and handles
the file system and communications in response to system calls.
As an illustration of the way that the shell and the kernel work together, suppose a user types rm myfile
(which has the effect of removing the file myfile). The shell searches the file system for the file containing
the program rm, and then requests the kernel, through system calls, to execute the program rm on
myfile. When the process rm myfile has finished running, the shell then returns the Unix prompt
to the user, indicating that it is waiting for further commands.
The Shell
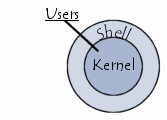 The shell acts as an interface between the user and the kernel.
When a user logs in, the login program checks the username and password, and then starts another program called the shell. The
shell is a command line interpreter (CLI). It interprets the commands the user types in and arranges for them to be carried out.
The commands are themselves programs: when they terminate, the shell gives the user another prompt.
The shell acts as an interface between the user and the kernel.
When a user logs in, the login program checks the username and password, and then starts another program called the shell. The
shell is a command line interpreter (CLI). It interprets the commands the user types in and arranges for them to be carried out.
The commands are themselves programs: when they terminate, the shell gives the user another prompt.
An experienced user can customise his/her own shell, and users can use different shells on the same machine. Faculty and students
working on turing and hopper have the bash shell by default.
The bash shell has certain features to help the user input commands.
Filename Completion - By typing part of the name of a command, filename or directory and pressing the [Tab] key, the bash shell will
complete the rest of the name automatically. If the shell finds more than one name beginning with the letters you have typed, it will beep,
prompting you to type a few more letters before pressing the tab key again.
History - The shell keeps a list of the commands you have typed in. If you need to repeat a command, use the arrow keys to scroll up and
down the list or type history for a list of previous commands.
Files and Processes
Everything in Unix is either a file or a process.
A process is an executing program identified by a unique PID (process identifier).
A file is a named collection of data. They are created by users using text editors, running compilers, etc.
Examples of Files:
- a document (report, essay etc.)
- the text of a program written in C++
- instructions comprehensible directly to the machine and incomprehensible to a casual user, for example,
a collection of binary digits (an executable or binary file)
- a directory, containing information about its contents, which may be a mixture of other directories
(subdirectories) and ordinary files. Equivalent to a folder in Microsoft Windows.
 The shell acts as an interface between the user and the kernel.
When a user logs in, the login program checks the username and password, and then starts another program called the shell. The
shell is a command line interpreter (CLI). It interprets the commands the user types in and arranges for them to be carried out.
The commands are themselves programs: when they terminate, the shell gives the user another prompt.
The shell acts as an interface between the user and the kernel.
When a user logs in, the login program checks the username and password, and then starts another program called the shell. The
shell is a command line interpreter (CLI). It interprets the commands the user types in and arranges for them to be carried out.
The commands are themselves programs: when they terminate, the shell gives the user another prompt.